| Title of unit/s | Employment Law |
|---|
1.1 The aims and objectives of employment law.
According to Avado (2020), employment law is a collection of laws and rules that regulates the relationship between employers and employees in an organization. The law governs what employers can ask their employees to do, what employers can expect from employees and the rights and freedoms of employees at work.
As per the European law, the purpose of employment law in organization incudes:
- Equal Treatment. It provides legal protection to both employees and employers. Also, it protects employees from unfair treatment by the employer as stipulated in the Equality Act 2010.
- Social Justice. Is based on equality. It ensures employees in the lower earning bracket enjoy equal opportunities and employment rights such as maternity leave and medical leave.
- This law ensures that all employees are subjected to the same laws guiding selection, recruitment, dismissal and salary payment by the employer.
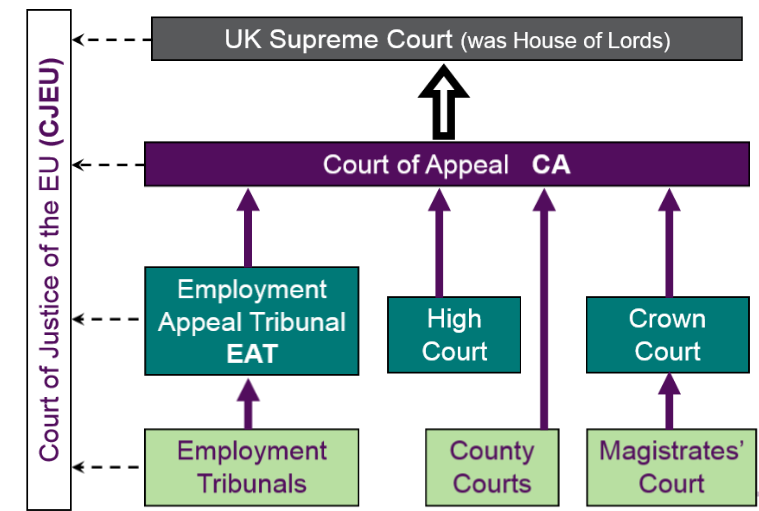
1.2 The role played by tribunals and other courts in the UK in enforcing Employment Law
Employment tribunals deal with claims raised by employees against their employers. For instance, claims relating to unfair and wrongful dismissal, unequal pay, discrimination or wage deductions.
There are two categories of Employment Law in the UK; Private and Civil law. Complaints and claims raised by employees such as discrimination, unequal pay and unfair dismissals by their employers are heard by the employment tribunal whereas the ordinary civil courts deal with cases such as accidents in the workplace.
(CIPD, 2020)
According to Pearson’s Chamber Law, 2017 an employee is entitled to raise a claim after termination of an employment contract and the claim must be made within three months of the termination. The Tribunal ensures the Advisory, Conciliation and Arbitration Service (ACAS) code is followed by both the employer and the employee. Tribunals are obliged by the decisions of the Employment Appeal Tribunal (EAT), Supreme Court, and Court of appeal to consider any new cases.
The UK justice system supports appeals against decisions made to the employment appeal tribunal. For instance, Pimlico vs. Smith case, “An appeal against a decision that the claimant, was claiming for disability discrimination, was a worker rather than self-employed. Appeal dismissed” (Employment Case Update, 2017).
- To begin with a claimant must first raise a claim to the Employment Tribunal (ET) including specifications and reasons for the claim. The claimant must include an Employment Tribunal document specifying an earlier conciliation process.
- Preliminary hearing is made prior to the main tribunal hearing headed by an employment tribunal judge. The tribunal basically comprises the employment tribunal judge and two members during the hearing process.
- Tribunal hearing begins either a preliminary or full hearing
- The tribunal looks at alternative ways of settling the claims and the settlement agreement.
1.3 Ways of settling disputes before and during the Employment Tribunal process
According to the American .bar.org, (2020), dispute resolution involves all those processes that can be used to resolve a conflict, claim or dispute. Dispute resolution in every organization is essential to enhance productivity and efficiency among employees and employers in an organization. There are various ways adopted to settle disputes within organizations such as;
- Arbitration
Arbitration involves independent individual deciding cases of unfair dismissal, makes conclusive decisions on a dispute, settles individual disputes and also solves all employment disputes within an organization. (Acas.org.uk, 2020)
The pros of arbitration are:
- It is more effective and faster than litigation in employment tribunal courts.
- Flexible and Inexpensive
The cons of arbitration are:
- It is inconsistent.
- Parties waive their rights and give full power to the judge to decide the case when the arbitration is binding.
- Mediation
Is a technique used for resolving disputes in an organization between employers and employees. According to the CIPD, mediation has the capacity to: boost communication and better relationship among employees, assist workers to emphasize with each other’s emotions and situations and lastly, assisting parties involved in conflicts to hold open conversation in settling their claims and disputes.
The pros of mediation are:
- Inexpensive for both parties involved.
- Flexible in producing acceptable solutions and settlements of the claim
The cons of mediation are:
- Mediation process could fall through.
- If one party fails to listen or fail to mutually agree then the case would end up in court (Lawshelf.com. (2019).
2.1 The importance of ensuring that the recruitment and selection process of new employees is fair.
In the UK all forms of discrimination in the workplace by employers and employees are managed by the Equality Act 2010. This Equality act 2010 has nine characteristics that it protects; maternity leave, disability, race, religion, gender realignment, marriage sex and sexual orientation (Avado, 2020)
Employers are advised through ACAS to avoid any form of discrimination relating to equality act, 2010 especially during recruitment, selection and job advertising process of new employees (Acas.or.uk)
Discrimination under Equality Act, 2010 can take any of the following forms;
- Direct
- Indirect
- Associative
- Perceptive
- Harassment
- Victimization
For instance, during recruitment of new workers, employers should not discriminate against any of the protected characteristics under the equality act. Employers must not inquire about private matters of the interviewee such as the matrimonial status and ethnic customs. Similarly, employers should avoid hiring based on body shape and appearance.
CIPD mentions that direct discrimination occurs when an individual is considered less favorable than others during the recruitment period due ones characteristic. Therefore according to Avado (2020), the claimant must be able to indicate that he or she was treated differently due to one of the characteristics in the equality act, 2010.
Indirect discrimination occurs when an employer of an organization puts specific people at a protected characteristics at a disadvantage position to prevent them achieve a targeted objective (Avado, 2020)
2.2 How a contract of employment is created
There are five stages in employment contract creation;
- Offer
According to CIPD, a job offer is a binding contract in form of a formal letter that stipulates the main terms being offered by an employer to a new employee. It is legally binding once the new employee accepts the job offer.
- Acceptance
It is when the employee accepts the job offer, thus making the offer official and legally binding.
- Intentions to create legal relations
It specifies that the contract is legally binding between the employer and the new employee
- Consideration
It specifies what both the employer and employee to offer one another in the contract.
- Certainty as to terms
It simply outlines the legal requirements of the offer subjected to acceptance. It is usually clear and precise.
3.1 Laws to be aware of as organizations change and develop
Contracts legally bind agreements between employers and employees, thus cannot be changed without agreement of both parties included. Contracts made between the employers and employees mainly include agreements of working hours or salary payment range.
Process followed when varying a contract of employment
- Collective agreements. Employers are required to write to their employees first to inform them of any changes in the contract. The changes my alter terms of employees written statements such as working hours or pay.
- Flexibility clause. The employer is guided by terms in the contract which gives the employer the right to alter the condition of nay employer such as relocation.
- Changes of employer. If an employee shifts to a different employer then the former employer can issue a new written statement. This does not apply in a case whereby the organization business name changes or a new employer but no change in the agreement terms then no need for a new written statement.
- Disciplinary measure. The employer has a right to change the terms and condition of the agreement of an employee such as demotion in case of disciplinary measures against that particular employee (gov.uk, 2020)
3.2 Main Requirements of Redundancy Law
Redundancy occurs when an organization is on liquidation. This happens when the organization is close to bankruptcy thus it opts to sell its assets to reduce costs.
According to the employment rights act 1996, it considers reasons for redundancy in section 139 as; the employer intending to cease operations of the organization in which employees were employed.
Redundancy affects the morale, motivation and productivity of the employees in an organization. Employers should thus consider the following steps in reducing redundancies.
- An organization should consider putting on hold some activities such as overtime, new the recruitments to save on costs.
- To seek assistance to determine the number of workers affected and the reason for redundancy dismissals
- Redundancy selection. Weather to dismiss employees with regards to attendance, disciplinary action or performance records
- Alternative employment. The possibility of creating alternative employment to redundant workers
- Redundancy payment. Costs to be considered either direct or indirect to pay redundant workers.
- Notification of dismissal to be done in writing to all employees facing redundancy.
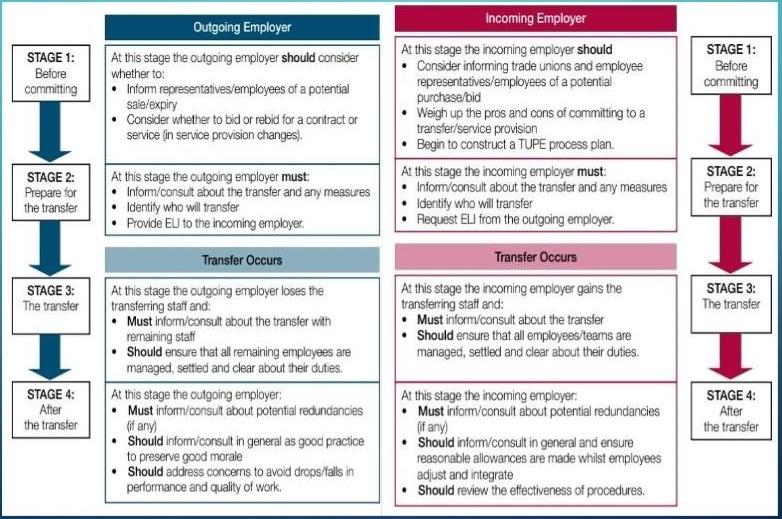
3.3 Requirement for addressing Transfer of Undertakings Protection of Employment (TUPE)
Protection of Employment Regulations 2006, as amended by “Collective Redundancies and TUFE Amendment Regulations 2014” (ACAS, 2020) specifies two scenarios of transfer undertaking as per CIPD guide;
- Transfer of a business to a new employer
- Change of service provision (CIPID guide, 2020)
Transfer Undertaking Process
TUPE varies depending on the form of transfer, either if it is a business transfer or a service provisional change. CIPD stipulates the following main factors to be considered during a transfer undertaking process
- In this stage, affected employees by the transfer undertaking are identified.
- The outgoing employer informs in advance the employees affected about the transfer. This is very crucial since failure of informing the employees in advance can subject the employer to compensate the employee if a claim is filed.
- Staff consultation. Both the outgoing and incoming employers make consultative meetings with all employees before the transfer is effective. This should offer time to conduct fair election to fill replacements of vacant positions.
- Employee Liability. Affected employees by the transfer must be identified earlier so that the outgoing employer can give the incoming employer the information at least 28 days prior to the transfer. Identities of employees, statement of particulars and the collective agreements, disciplinary action details and any legal action details should be prepared earlier by the outgoing employer.
- The incoming employer ought to plan and consult pension payment measures and plans.
- TUPE
(ACAS, 2020)
In the UK, any automatic unfair dismissal claim leads to either Basic and Compensatory award payment. Basic calculation award which is ordered by the Tribunal of up to 16,140 pounds. Compensatory award presently the statutory cap of 88,519 pounds, or a 52 weeks gross salary as the lowest. (landaulaw.co.uk, 2020)
4.1 Rights of Employees during employment
Under the UK laws, there are a variety of stipulated laws and regulations that define employee’s rights and entitlements;
- The Employment Right Act 1996
- Health and Safety at Work
- Working time regulation 1998
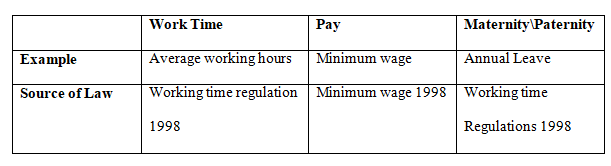
- Working Time
In UK, the working Time Regulations Act, 1998 stipulates that the allowed working hours for employees is approximately 48 hours in a week. Exception is only considered for employees in the army and the National police. (Gov.uk, 2020)
For instance, in a case between Hughes vs. Corps of Commissionaires Management (No2)(2011), The court of appeal ruled out that a guard working a 12 hour shift could start a rest break if the client interrupted the guard’s rest break by a cellphone call from the client (employmentupdates.co.uk, 2011)
- Pay
The UK government through the National Minimum Wage 1998 declared that the minimum wage rate per hour depends on the employee’s age. The rates are adjusted every April of the year. (Gov.uk, 2020)

(Gov.UK, 2020)
- Maternity and Paternity Leave
The Working Time Regulations 1998, specify that all employees are entitled to a minimum of not less than five weeks or approximately 28 days of paid annual leave per year (Gov.uk, 2020)
4.2 The major maternity, paternity and other family-friendly employment rights.
The following are legislations covering family-friendly rights
- Maternity and Paternity 1999
Every female employee is entitled to maternity leave of 52 weeks. Two weeks compulsory leave during birth of the child. The first 26 weeks of ordinary maternity leave (OML) and an addition 26 weeks of additional maternity leave (AML).
- Shared Parental Leave (SPL), 2014
Gets 50 weeks leave and 37 weeks of pay (CIPD, 2020). Can be available for work after handing notice to finish her maternity leave early
- Statutory Maternity Leave (SML)
An employee is entitled to get a statutory maternity leave and must give the employer the correct notice (Gov.uk, 2020). It is payable for 39weeks. 90% of the salary is paid for the first 6 weeks and the rest 145.14 pounds paid for the following 33weeks (CIPD, 2020).
To qualify for SMP, one must be an employee not a worker ,earn an average of at least 118 pounds per week, provide proof of pregnancy ,give the notice period and have worked for a period of at least 26weeks (Gov.uk, 2020).
- The Work and Families Act 2006
Employees on maternity leave are allowed to work for 10 days without losing maternity pay.
- Children and Families Act 2014
Under this act employees can get 52 weeks of Statutory Adoption Pay (SAP) of which 39 weeks are payable.
5.1 The major requirements of health and safety law.
Under the Health and Safety at Work Act (HSWA) 1974, and Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999, employees are required by law to ensure health, safety and welfare at work.
Both employees and employers have the responsibilities to ensure they operate on a healthy and safe work environment as set by the HSWA.
Duties of the employers:
- Employ competent and safety-conscious staff
- Provide a safe place and system of work
- Provide adequate plant and equipment. (CIPD, 2020).
Duties of the employees are:
- Cooperate with employers to attain the health and safety requirements
- Make health and safety their paramount priority. (CIPD, 2020)
5.2 The significance of implied duties as regards the management of employees at work.
In accordance to CIPD, employers have a duty to provide a safe work environment to employees by:
- Publishing health and safety policy guidelines
- Establish a health and safety committee.
- Set up continuous risk assessments
- Monitor and improve safety arrangements
- Conduct constant training (CIPD, 2020).
Employers should communicate the above clearly to the employees and make the information easily accessible. Risk assessments that identify potential hazard should be under taken regularly. Moreover employers are required to keep record of their risk assessments and set up emergency procedure (CIPD, 2020). Furthermore, employees are protected under the Equality Act 2010 from victimization, harassment and bullying related to a protected characteristic.
Under the Health and Safety regulations, all employers have responsibilities to ensure their employees operate in a safe conducive environment; failure to this it will be within the employee’s right to claim constructive dismissal.
The employer may terminate the employee’s contract when the employee breaches the duty of implied trust and confidence.
The employee must communicate effectively and clearly with the employees, update the policy and procedures, involve employees with work environment surveys and undertake risk assessments on regular basis to void a breach in trust and confidence.
5.3 Principles of the law on freedom of association.
In accordance to article 11 of the Human Rights Act 1998, states that, freedom of association entitles people the right to form societies, clubs, and associate with people individually, but without interfering with the government as part of the trade union or protest to protect their interests (Equalityhumanrights.com, 2020).
However for this to happen, conditions should be in accordance with the following Employment Law;
- The action must be supported by a ballot
- The action must be lawfully called
- The union must notify the employer of its intention to take action
- The action must take place within a specified period after the ballot
- Industrial action must be taken in contemplation or furtherance of a trade dispute
- The ballot itself must satisfy a series of procedural requirements (Employment Law Watch, 2020).
6.1 Requirements for addressing disciplinary actions relating to capability and misconduct issues.
Dismissal occurs when an employee’s contract is terminated abruptly with or without notice due to valid reasons such as misconducts, incompetence or redundancy. For the dismissal to be legal the employer follows the fair dismissal processes specified by the Employed Right Acts and ACAS. They are:
- Raise and get involved with the dilemma promptly, and act consistently.
- Consideration is given to suspend the employee while investigation takes place.
- During the investigation, an impartial party is present to establish the facts and provide evidence.
- The concerned employee is to be invited to a disciplinary hearing, and copies of evidence gathered throughout the investigation. The employee has the right to respond to the accusation prior to the decisions are made.
- The decision is to be announced to the employee.
The employee can be accompanied by a trade union representative or a colleague during this grievance meeting. He can also appeal against a decision which is heard by a superior manager (Avado, 2020)
According to the UK Employment Act 1996 and ACAS, there are five fair reasons employers can use to dismiss employees.
- Misconduct
- Employee capability such as Incompetency
- Redundancy
- Illegality
- Other Substantial Reason
6.2 The right for employees to be accompanied during formal disciplinary and grievance hearings
All employees of an organization have the right to be accompanied by either a trade union representative or a work colleague during a disciplinary meeting as stipulated in section 1999. The duty that this trade union representative or colleague is to address the meeting when needed to, summarize key points but not to speak on behalf of the employee (Legislation.gov.uk, 2019).
Reference List
Acas.org.uk.(2020)Arbitration advice and guidance | Acas. [online] Available at: https://www.acas.org.uk/index.aspx?articleid=1711 [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
Acas.org.uk. TUPE. (2020). [online] Available at: https://www.acas.org.uk/media/4012/Handling-TUPE-transfers-The-Acas-guide/pdf/Handling-TUPE-Transfers-The-Acas-Guide.pdf [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
Americanbar.org. (2020). Dispute Resolution Processes. [online] Available at: https://www.americanbar.org/groups/dispute_resolution/resources/DisputeResolutionProcesses/ [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
Campus.avadolearning.com. (2020). AVADO Learning Platform | AVADO Learning Platform. [online] Available at: https://campus.avadolearning.com/mod/book/view.php?id=190901&chapterid=54015 [Accessed 27 Sep. 2020].
Campus.avadolearning.com. (2020). AVADO Learning Platform | AVADO Learning Platform. [online] Available at: https://campus.avadolearning.com/mod/book/view.php?id=190901&chapterid=54017 [Accessed 27 Sep. 2020].
Campus.avadolearning.com. (2020). AVADO Learning Platform | AVADO Learning Platform. [online] Available at: https://campus.avadolearning.com/mod/book/view.php?id=190921 [Accessed 27 Sep. 2020].
Cipd.co.uk. (2018). A GUIDE TO TUPE TRANSFERS. [online] Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/Images/7697-a-guide-to-tupe-transfers-web_tcm18-44310.pdf [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
CIPD. (2020). Employment Tribunals | Factsheets | CIPD. [online] Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/emp-law/tribunals/factsheet [Accessed 24 Sep. 2020].
CIPD. (2020). UK Court System & Employment Law | Factsheets | CIPD. [online] Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/emp-law/about/court-system [Accessed 24 Sep. 2020].
CIPD. (2020). UK Court System & Employment Law | Factsheets | CIPD. [online] Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/emp-law/about/court-system [Accessed 24 Sep. 2020].
CIPD. (2020). Contracts of Employment | Factsheets | CIPD. [online] Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/emp-law/terms-conditions/contracts-factsheet [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
CIPD. (2020). Redundancy | Factsheets | CIPD. [online] Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/emp-law/redundancy/factsheet [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
CIPD. (2019). Holiday Entitlement Cases | CIPD. [online] Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/emp-law/holidays/entitlement-cases [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
CIPD. (2019). Working Time Cases | CIPD. [online] Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/emp-law/working-time/cases [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
CIPD. (2020). TUPE (Transfer of Undertakings) | Factsheets | CIPD. [online] Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/emp-law/tupe/factsheet [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
CIPD. (2020). Maternity, Paternity & Adoption Rights | Factsheets | CIPD. [online] Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/emp-law/maternity-paternity-rights/factsheet [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
CIPD. (2020). Health & Safety at Work | Factsheets | CIPD. [online] Available at: https://www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/fundamentals/emp-law/health-safety/factsheet [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
Employment Cases Updates, Pimlico Plumbers & Anor v Smith [2017] EWCA Civ 51. [online] Available at: https://www.employmentcasesupdate.co.uk/site.aspx?i=ed35083 [Accessed 24 Sep. 2020].
Employment Law Watch. (2020). Trade Union Bill Published | Employment Law Watch. [online] Available at: https://www.employmentlawwatch.com/2015/07/articles/employment-uk/trade-union-bill-published/ [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
Equalityhumanrights.com. (2020). Article 11: Freedom of assembly and association | Equality and Human Rights Commission. [online] Available at: https://www.equalityhumanrights.com/en/human-rights-act/article-11-freedom-assembly-and-association [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
GOV.UK. (2020). Employment tribunal procedure rules. [online] Available at: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/employment-tribunal-procedure-rules [Accessed 24 Sep. 2020].
Lawshelf.com. (2019). Advantages and Disadvantages of Mediation – LawShelf Educational Media. [online] Available at: https://lawshelf.com/courseware/entry/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-mediation [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
GOV.UK. (2020). National Minimum Wage and National Living Wage rates. [online] Available at: https://www.gov.uk/national-minimum-wage-rates [Accessed 28 Sep. 2020].
Legislation.gov.uk. (2019). Employment Rights Act 1996. [online] Available at: http://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1996/18/part/I [Accessed 26 Sep. 2020].
Legislation.gov.uk. (2019). Employment Rights Act 1996. [online] Available at: http://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1996/18/part/I/crossheading/right-to-statements-of-employment-particulars [Accessed 26 Sep. 2020].
Legislation.gov.uk. (2019). Employment Rights Act 1996. [online] Available at: http://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/1996/18/section/139 [Accessed 26 Sep. 2020].



