Table of Contents
Task One – Strategic Planning Meeting Report
As your report is being prepared for a formal senior management meeting, it should be written in formal business report format and style.
Your report is to be provided to BMC’s forthcoming Strategic Management Planning meeting where the main priority is to discuss implementing the new business strategy. The team is made up of mainly operational managers who have limited knowledge and understanding of the connections between organisational structure, strategy, and the wider business environment so the CEO has asked that your report should include an understanding of the connections between organisational structure, strategy, and the business operating environment.
The report must therefore include:
- An evaluation of the advantages and disadvantages of two different types of organisational structures in different types of organisations, the range of products, services and customers
- Associated with each, and how they link to organisational purpose. (AC 1.1)
- An analysis of the way in which organisational strategy should be linked to products, services, customers and revenue (AC 1.2)
- An analysis of the current and ongoing impact on organisations of the range of external
factors and trends. (AC 1.3) - An assessment of two current issues and causes that identify key priorities within organisations that will affect product/service delivery, and the impact this may have on people practice and solutions. (AC 1.4 & AC 3.3)
- An explanation of the ways in which people practices can impact on organisational systems and structures, and therefore affect the effective employment, management and development of people (AC1.5)
- An exploration of the impact that technology has on people, work and working practices,
and the current and emerging scale of the use of technology within organisations. (AC 1.6)
Task Two – Presentation Pack
The CEO has also asked you to prepare a presentation to the managers prior to their formal Strategic Management Planning meeting to position them for their meeting. The focus is to give theoretical understanding of organisational culture and workplace behaviour and how people practices should support the achievement of business goals and objectives. The presentation pack needs to include presentation slides and supporting notes.
The presentation must include:
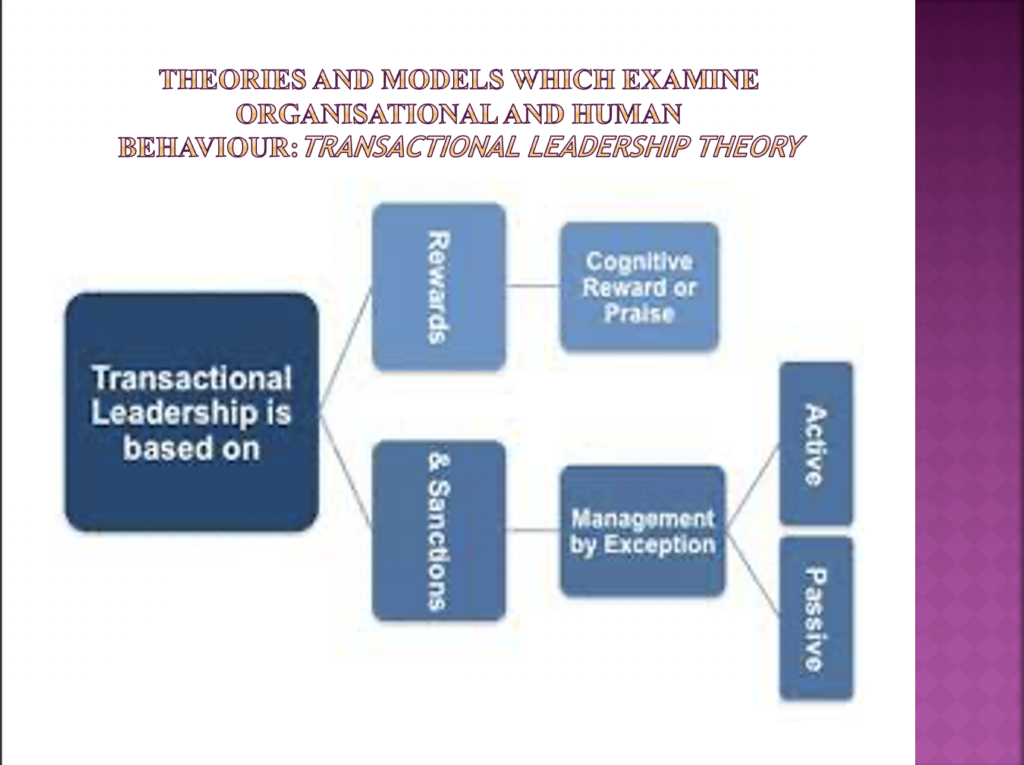
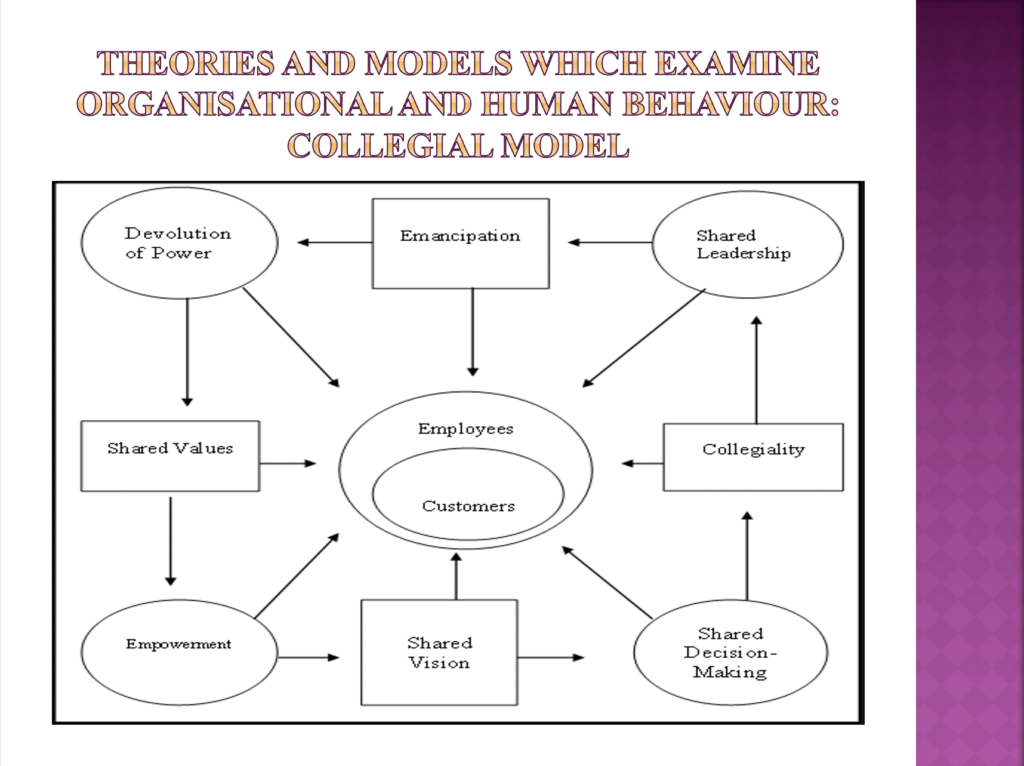
- An explanation of the principles of different approaches, theories and models of organisational and human behaviour that illustrate the factors that can influence how individuals, groups and teams contribute to organisational success. (AC 2.1)
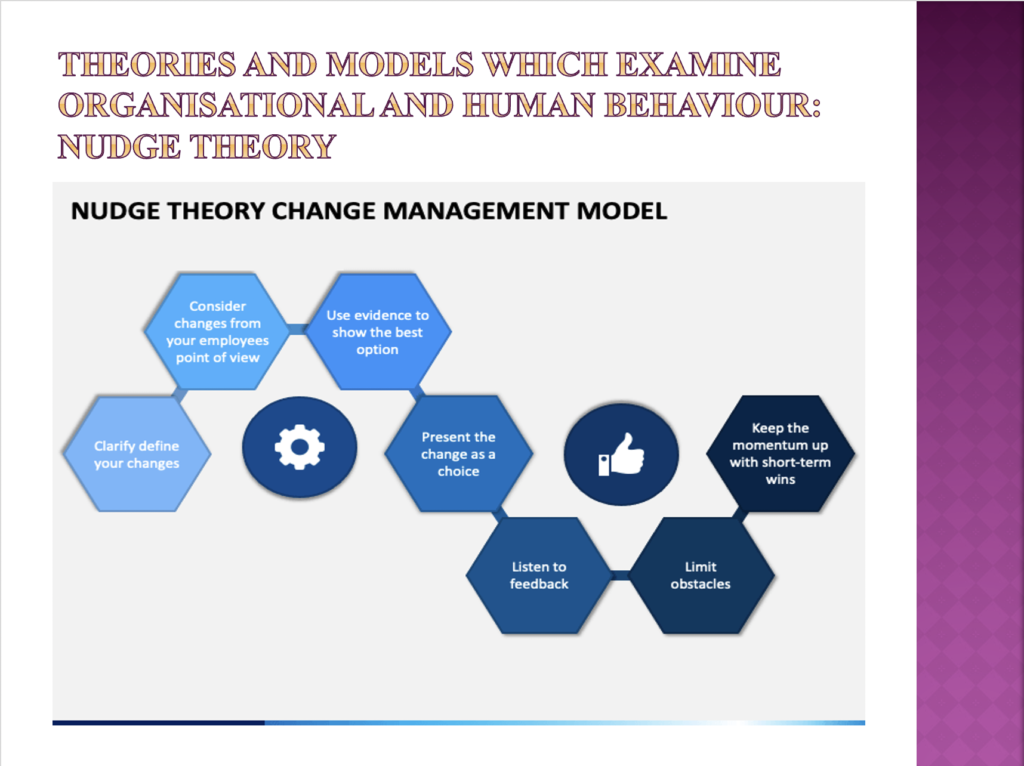
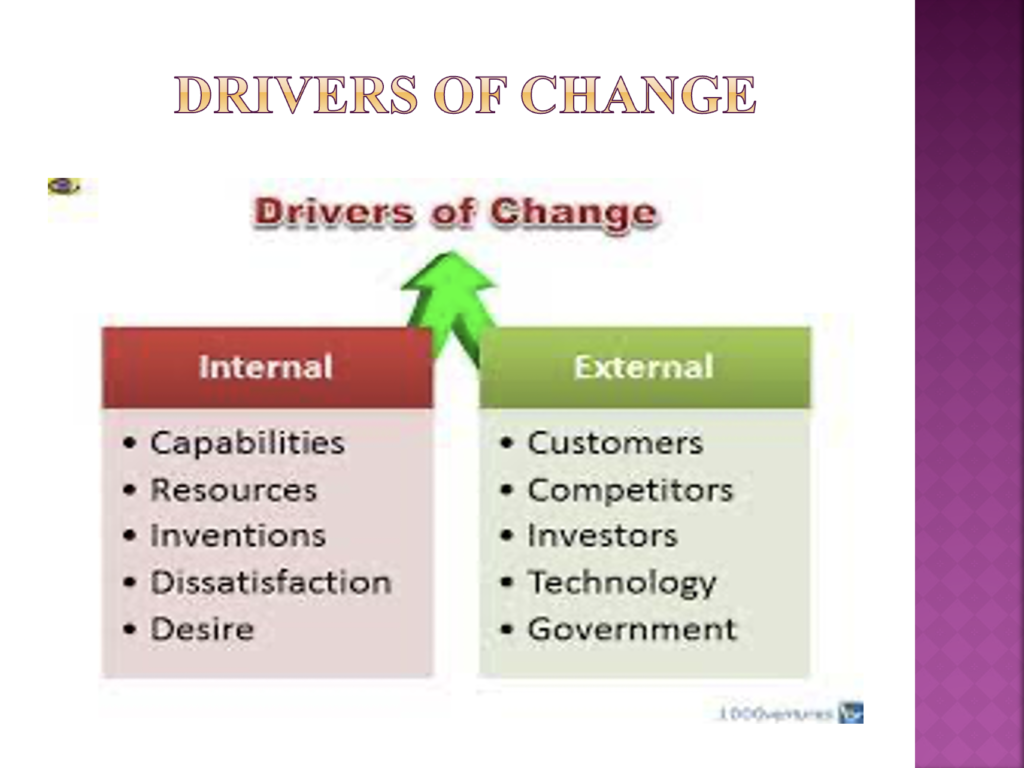
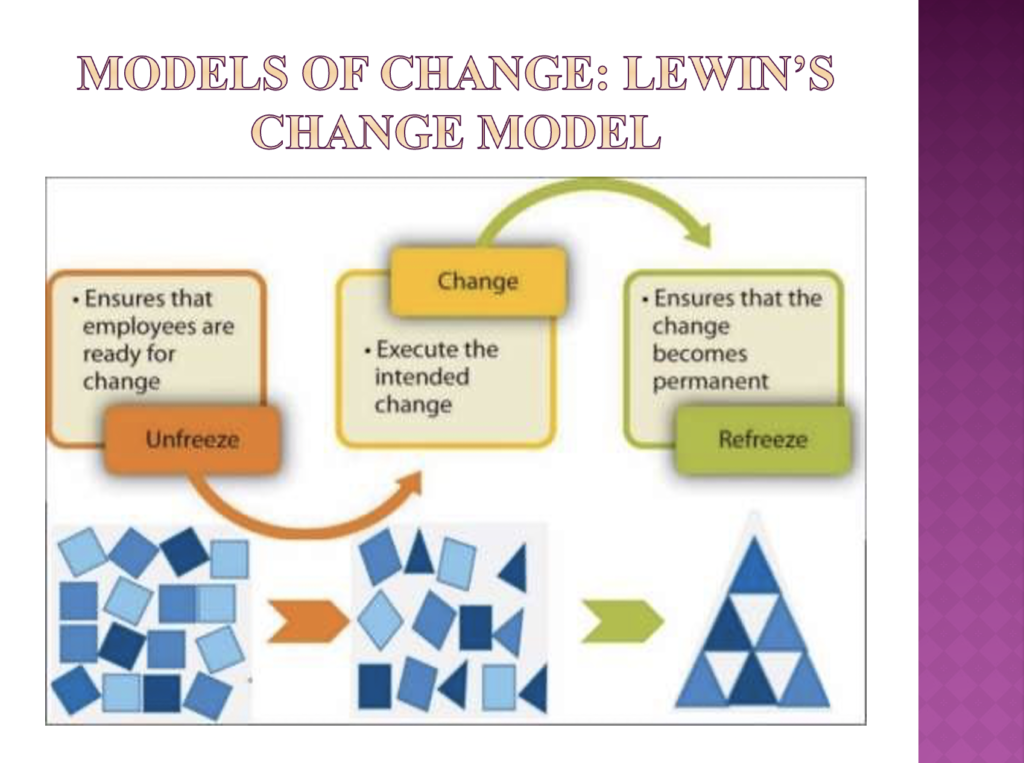
- An identification of the main drivers of change in organisations, and using at least two established models, an explanation of how people might experience change (AC 2.2)
- An explanation of the steps that can be taken to increase diversity and inclusion in your work, and the implications for a positive and inclusive culture of not taking these steps (AC2.3)
- Using examples from your experience and current good practice concepts, an explanation of the positive and negative ways in which people practices can affect organisational culture and behaviours. (AC 2.4)
- An assessment of the importance of wellbeing in the workplace and identification of the different factors affecting wellbeing that can impact physically and psychologically and upon relationships, affecting health, commitment and performance. (AC 2.5)
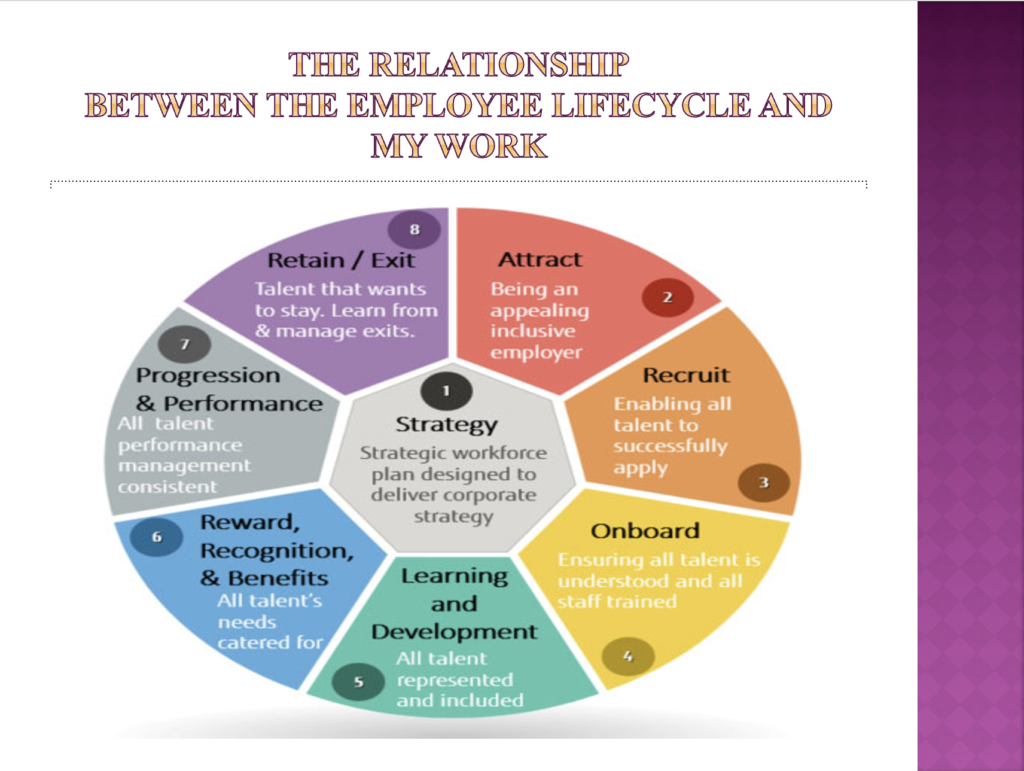
- A critical evaluation of your experience of work and how this illustrates and supports the concept and principles of employee lifecycle (AC 3.1)
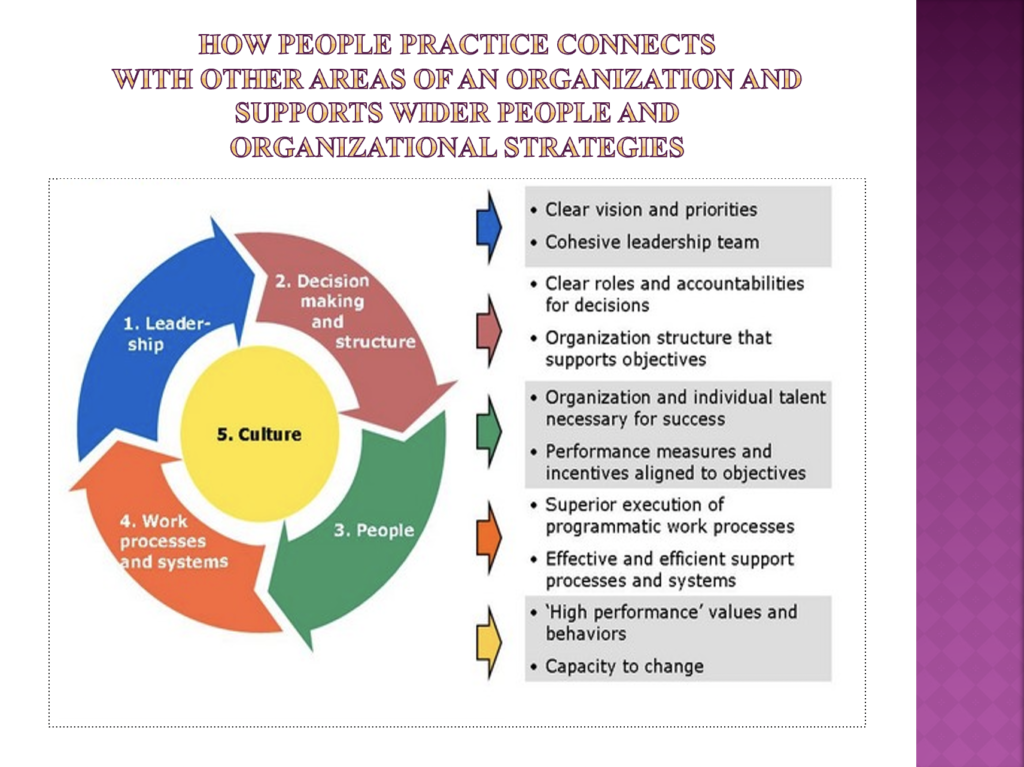
- Explains both the strategic and operational links and support between people practice and other organisational functions. (AC 3.2)
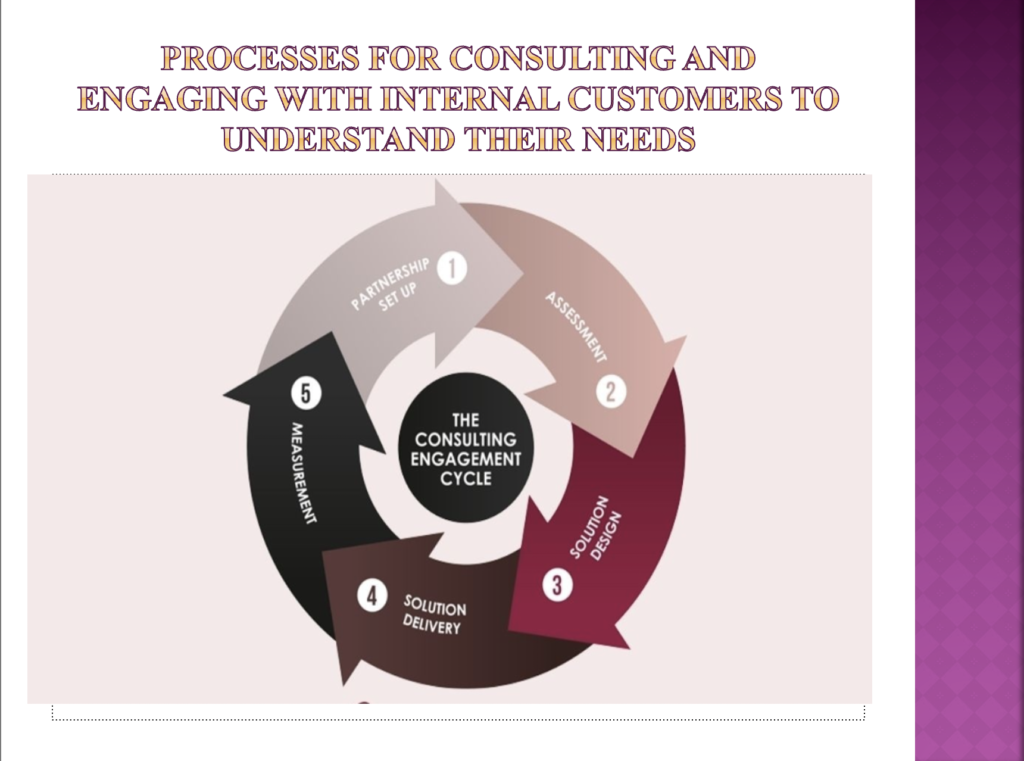
- Explores the principles of different approaches for engaging with internal customers to establish their needs (AC 3.4)
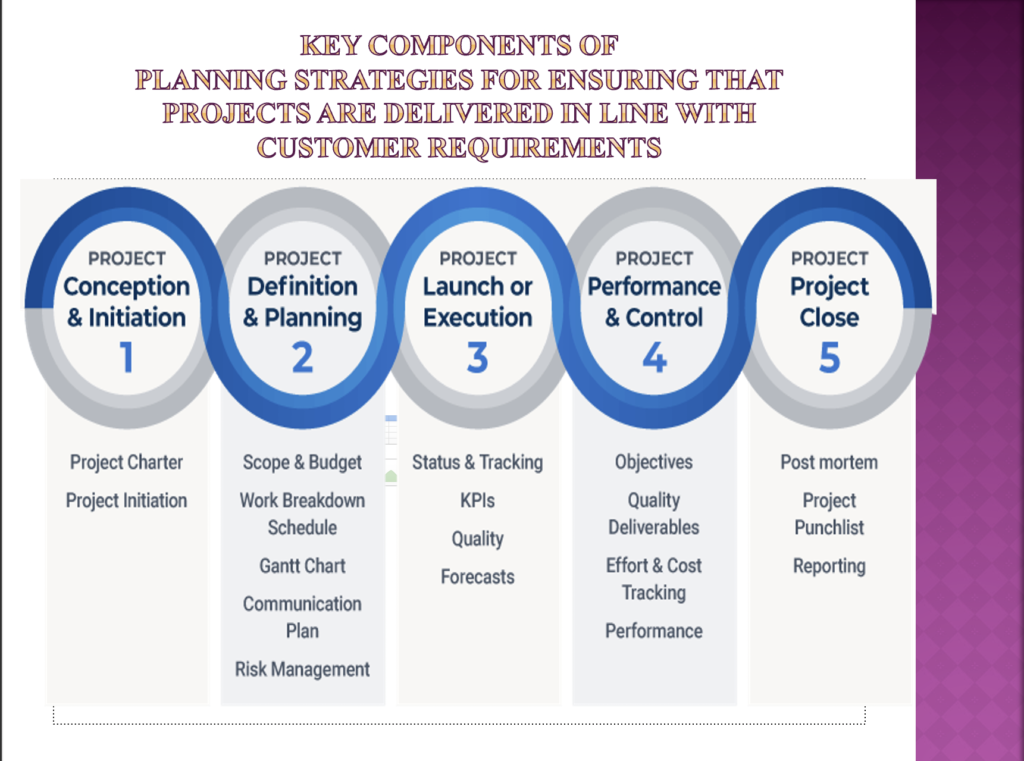
- Explains the key components of project planning strategies that can be used for ensuring projects are delivered in line with customer requirements. (AC 3.5)
It is essential that you refer to academic concepts, theories and professional practice for the tasks to ensure that your work is supported by analysis. Please ensure that any references and sources drawn upon are acknowledged correctly and supported by a bibliography.
AC 1.1 Associated with each, and how they link to organisational purpose.
Matrix structure
This is an organizational structure whereby the reporting relationships are designed as a grid or matrix instead of the traditional hierarchy. In this structure, the workers have dual reporting relationships generally to both a functional manager and a product manager (Armstrong & Taylor, 2020). The employees are answerable to two or more managers rather than just one line manager overseeing every aspect of a job role.
Advantages;
This kind of organizational structure lets various work divisions communicate easily and cooperate on a project. Since the workforces are answerable to numerous line managers and not just to their respective functional managers, resolution of issues is undertaken more quickly, and organizational-wide relations are enhanced. There is also improved sharing of resources across all the firm’s departments and efficient development of the employees (Sharp & Green, 2020).
Disadvantages;
It requires excellent collaboration between the functional and project managers and has the likelihood of conflicting managerial instructions and dictates. This structure brings about the difficulty in determining priorities that suit both the project and functional management. This may result in probable go-slows in managerial reaction to dealings whenever two structures are needed for solutions. There is also the possibility of structural breakdown during crisis moments and high overhead costs in the firm’s management.
Divisional structure
This is whereby the firms are designed to divide into semi-autonomous units termed divisions. These divisions have control over their daily organization’s operations. However, they are still answerable to a centralised management that provides the overall strategy for the company and coordinates its application among the divisions. Large multinational corporations typically use this structure (Beevers, Hayden & Rea, 2019).
Advantages;
For the reason that every single division is semi-autonomous, operational decisions are made by workers nearer to the exact issues and challenges. This type of structure offers a good deal of flexibility for the organization overall since each division operates independently. The labour force will specialize in technical know-how and skills best suited for problem resolutions. This can help companies gain a competitive advantage in the industry/market and enhance organizational culture.
Disadvantages;
It is not suitable for smaller firms, and lack of communication among the divisions may derail the growth and performance of the organization. It calls for many experts, hence costly to establish and implement. The heads of divisions are autonomous in executing their day-to-day tasks; as much as this accelerates decision making and actions performed by the division, it can generate corruption. Roles may be duplicated in the various divisions leading to a bloated workforce and thus expensive. This structure can produce aggressive and unhealthy competition as each division strains to outdo the other (Houghton & Young, 2019).
AC 1.2 An analysis of the way in which organisational strategy should be linked to products, services, customers and revenue
There are a lot of impacts of strategic planning on the performance of an organization, like excellent product quality, substantial variations in profit levels, huge client patronage, and upsurges in volumes of sales. The intensity of strategic planning is influenced by the management, structural and environmental dynamics (Houghton, 2020). Business strategies are the basis of survival in a competitive business climate and must be well crafted. A strategic plan is impractical unless implemented successfully, which calls for a good appraisal plan. For effective implementation of a strategy, firms ought to be aligned towards the recruitment of talented and motivated employees, who, grounded upon their accomplishments, should be promoted to higher hierarchical levels of management. The organization’s business leaders and all other workforces must have a vision for the development course of their company. This will promote the development of a culture of high performance. Additionally, the growth of financial autonomy will enhance the flexibility and ability to execute strategy.
Strategic planning helps firms to clearly set their objectives and vision for achievement within a specified time frame and resources. Organizations have to lay out blueprints, policies, and design structures for operations in order to realize their vision. Project management skills come to play in setting out and fusing organization structures (Beevers, Hayden & Rea, 2019).
Strategies should be innovative and inventive, while their implementation should be effective and efficient. A rapid and effective response will improve monitoring and evaluation and assist in executing the strategy and circumvent or minimize failure. Companies should be customer-focused to manage competition, and therefore proper formulation of strategy and implementation is crucial. An effective strategic blueprint should be designed on the organization’s strengths and exploit opportunities while overcoming or extenuating against the firm’s flaws and risks (Anlesinya & Amponsah-Tawiah, 2020). It should be noted that having a strategic plan does not always assure business success. Still, a well-developed, inventive, and creative strategy that is well implemented will ensure success.
AC 1.3 An analysis of the current and ongoing impact on organisations of the range of external factors and trends.
The external factors and trends that are impacting organizations: social and cultural trends, technological advancements, demographic trends, and political dynamics. In response to the ever-changing tastes and preferences of the customers, firms are gradually adapting to a production pattern that suits best the interests and needs of their clientele. Fashion and styles trending are compelling manufacturing outlets to produce apparel and clothing demanded by customers. Seasons necessitate what is offered for sale at the market. Improvements in technology, automation, and mechanization are changing the production patterns in organizations. Firms are adopting machines to produce goods or services; robotics and artificial intelligence take over human capital in companies (Parida, Sjödin & Reim, 2019). Biometrics and digitalized systems manage the employee life cycle in organizations ranging from sourcing, recruitment, payroll management, work supervision, and pensions and retirement benefits administration.
Political economy shapes the workplace policies and regulations used to govern and run organizations. This influences governments’ decisions regarding business regulations, labour laws, and even workers’ affiliations and relations to trade unions. Demographic shifts and population migration across regions influence the workforce composition and recruitment patterns in various organizations and the products to be produced and traded upon.
Another external factor is the massive growth and usage of social media platforms, which positively impacts business corporations since it offers them an avenue to market their goods and services and promote their public image and brand. Seasonal and climatic, and in some cases ethnic forces are also impacting the demand for some particular products in the market (Bombiak & Marciniuk-Kluska, 2019). As a result the business entities are compelled to respond in order to meet their clients’ needs for the period of such spells or terms. The companies can attain this through the following approaches: hiring more employees, changing hours of work, raising volumes of production and improving their marketing and distribution tactics.
This will ensure a continuous and uninterrupted supply of goods and services in the market.
The great and diversified demographics provide both opportunities besides challenges for business corporations (Sharp & Green, 2020). Legislative frameworks can impact revenue streams (by raising taxation and regulation), business aims, or competitiveness. Globalization and fluctuation in international market prices of commodities and wages also impact how companies operate. This affects their pricing and international trade policy. The economic setup entails factors that can impact the purchasing power of consumers as well as their expenditure patterns.
AC 1.4 An assessment of two current issues and causes that identify key priorities within organisations that will affect product/service delivery, and the impact this may have on people practice and solutions.
As it stands now, organizations are adapting to the current business atmosphere for them to cope and ensure business continuity. Amidst the Corona disease worldwide pandemics, firms have been forced to restructure by some firms scaling down their workforces, others closing down branches, and even others changing their production/service styles and approaches. So many organizations have prioritized and channeled more resources to promote remote working so in order to reduce physical interactions of employees, thereby curbing the spread of the disease.
The current issue within organizations which may affect service delivery is high employee turnover. This is a scenario in which more employees leave a firm than those hired. Employee turnover rates may result from a wide range of internal and external factors. Internal factors include lack of motivation, job dissatisfaction, lack of career growth opportunities, structure and culture, etc. Some external factors include intense competition for labour resources, legal issues such as high taxation, which may increase the cost of production, government policies (Buhalis et al., 2019). BMC’s challenges with employee turnover are caused by an internal factor: job dissatisfaction. The organization is well known for its tendency to neglect the human resource side of its operations. It is mainly concerned with the expansion and production part. Human resources are the backbone of any company’s success. Therefore much attention is needed there. The stiff competition in the labour market has worsened the situation, with most skilled employees seeking other companies. The company should therefore prioritize changing the status quo. This can be done by increasing employee motivation. Employee motivation can be achieved through employee engagement. Employees feel part of the company when they are engaged in most decision-making undertakings. Therefore, the company should make sure that the workers are engaged and pleased with the company’s strategies and policies. This will give them something to work towards, hence improving motivation.
Clear communication between the management and the junior employees is an issue. Enhancing communication through open and honest conversation and constructive feedback can help improve the situation. Shortage of key talent is a current priority issue for firms in the labour market. Innovative and modern methods of running businesses are coming courtesy of technological advancements and innovations. Companies compete against each other to remain competitive in the market. They are rushing to train their staff to be IT compliant in line with the emerging trends in the tech world. Corporates are scouting for critical talents that are in missing in their firms. Personnel with expertise in machine learning, data science, analytics, remote sensor, artificial intelligence, and robotics are in great demand by organizations (Bombiak & Marciniuk-Kluska, 2019).
Companies are as well becoming more future-oriented. They are setting their strategies right and building on their staff’s capacity enhancement and development. This is to enhance their performance and also to keep them afloat with the current business trends (Houghton & Young, 2019). Mergers have been realized to help organizations reduce operations costs, improve profitability, and help the firms attain their other numerous objectives optimally and cost-effectively.
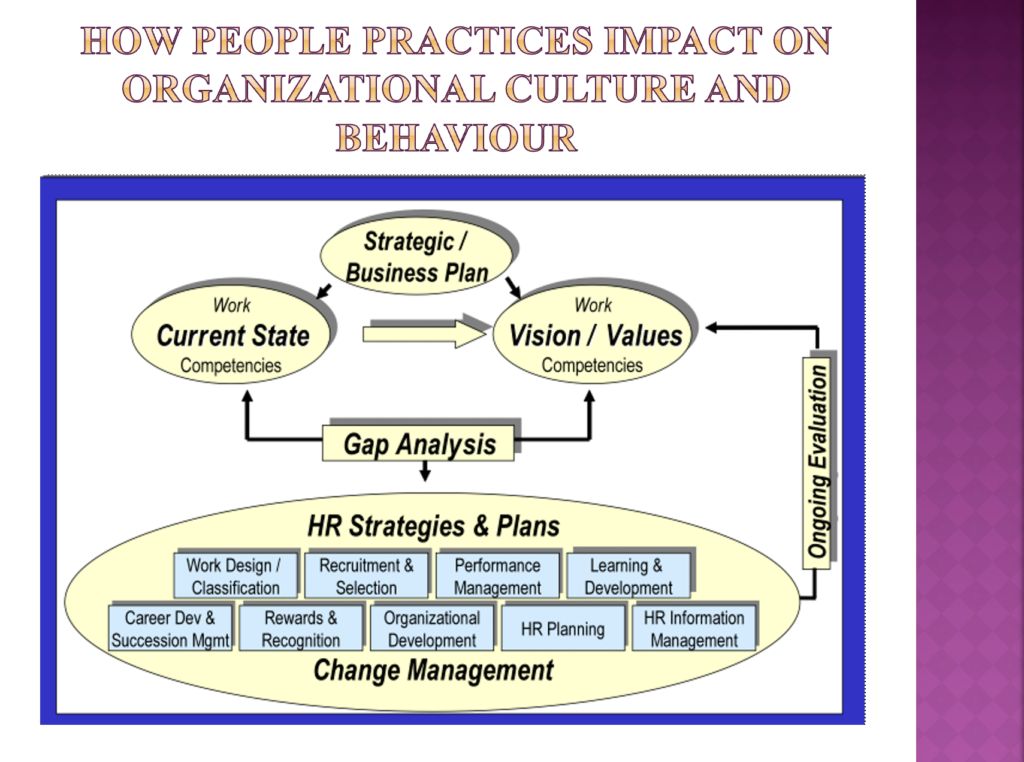
AC 1.5 An explanation of the ways in which people practices can impact on organisational systems and structures, and therefore affect the effective employment, management and development of people
People practices such as the creation of talent groups, development of personnel policies, analytics of people statistics, management of staff grievances, and recruitment of people; impact on the structure and systems of organizations in a number of ways. Firstly, these practices will determine how employees are classified according to their talent and expertise to execute varied roles and responsibilities (Beevers, Hayden & Rea, 2019).
The mechanisms that seek to coordinate the divisions of labor are known as organizational systems. The structure of an organization is similar to a skeleton: it determines spatial linkages and impacts power dynamics among its different components. The frame does not perform much work on its own; it only serves as a framework within which the corporation coordinates its resources to achieve its mission. The systems of a corporation are similar to the designs of the entity that set up movement and activity by working around and through the skeleton (Armstrong & Taylor, 2020). Recruiting, performance management, reward, data processing, performance assessment plus promotion, and grievances are only a few examples of people practices in the workplace that enable organization systems and structure to work.
Staffing is necessary for every organizational structure. Wise business leaders carefully analyze how the individual skills of the people and the positions fit together. The mere presence of a job description on a piece of paper does not imply that someone in that position will be capable or willing to accomplish the duties stipulated in the job description. Many senior managers are more ready to make structural modifications than human adjustments when the abilities of available employees do not fit the work needs of certain portions of the organizational structure. Both choices are obviously available, each with its own set of expenses. People practices are the methods and approaches we utilize throughout the employment lifetime. A good organization will use the best human resource management to ensure that the people practice in the organization is managed correctly (Beevers, Hayden & Rea, 2019). When the organizational structure best suits the organization, the people practices will be handled seamlessly.
AC 1.6 An exploration of the impact that technology has on people, work and working practices, and the current and emerging scale of the use of technology within organisations
Technology has developed to be an integral part of contemporary society, and firms need to be innovative to counter the emerging technologies. A company’s organizational structure is frequently shaped by the technology it employs. Batch-technology organizations are usually structured differently from continuous-process companies. Organizational structures for technologies involving highly interconnected elements differ from those using autonomous, distinct pieces. The sequence of tasks and the equipment and people available to do them may significantly influence the management of the firm. As a result of the rapid development of technology and satellite-based information systems, new organizational structures are being created in today’s digital age (Buhalis et al., 2019). Organizations have learned that technology is essential to effective recruiting in recent years. Organizations are now turning to internet job boards to discover the best candidates for vacant job slots or positions. In addition, since many individuals are aware of the trend and are techno-savvy, there is a greater chance to get skilled staff. Portals allow employers to provide all necessary information on employment contracts, careers, and personal growth to potential employees and job candidates.
Technology is taking over most activities that people were initially carried out at the workplace. Technological impact, for example, in the communication and manufacturing industries has exponentially augmented the production rate of commodities and improved tremendously the speed at which business takes place. Technology at work has helped employees become extra efficient compared to before. Payment for business transactions, products have become cashless. Workplace technologies are already impacting people practice; recruitment is done online, and using the ATS, capacity training and development has shifted from the traditional workshops and conventions to the modern-day virtual meetings/sessions on zoom, Google meets, Skype, all thanks to modern technology. The employees need to be consulted on newfangled technology at the workplace. They need to be the focal point in making decisions regarding technology adoption that will impact their job roles (CIPD, 2019).
AC 3.3
Adoption of advanced technologies at the workplace in service delivery is changing the way people practice ordinarily executes its role. In performing human resource data analytics, and performance-based evaluation programs to inform policy decision-making at the firm, the HR professional uses various management information systems. This saves time and cost and is user-friendly and straightforward to the personnel. This has enhanced service delivery and helped improve the performance of the employees and the organization at large. Strategies for better management of employees are developed and implemented promptly using reasonably practical approaches (Armstrong & Taylor, 2020).
The people practice will have to change how they deal with the staff at the workplace. In attempts to minimize operations costs, firms are closing some branches/offices and opting for remote working by their personnel. Technological innovations are enabling this. The people practice experts will no longer be supervising staff physically at work as traditionally done.
References / Bibliography
Anlesinya, A. and Amponsah-Tawiah, K. (2020), "Towards a responsible talent management model", European Journal of Training and Development, Vol. 44 No. 2/3, pp. 279-303. https://doi.org/10.1108/EJTD-07-2019-0114
Armstrong, M. and Taylor, S. (2020) Armstrong’s handbook of human resource management practice. 15th ed. London: Kogan Page.
Beevers, K., Hayden, D. and Rea, A. (2019) Learning and development practice in the workplace. 4th ed. London: CIPD Kogan Page.
Bombiak, E. & Marciniuk-Kluska, A., 2019. Socially Responsible Human Resource Management as a Concept of Fostering Sustainable Organization-Building: Experiences of Young Polish Companies. Sustainability, 11(4), p.1044. Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/su11041044.
Buhalis, D., Harwood, T., Bogicevic, V., Viglia, G., Beldona, S. and Hofacker, C. (2019), "Technological disruptions in services: lessons from tourism and hospitality", Journal of Service Management, Vol. 30 No. 4, pp. 484-506. https://doi.org/10.1108/JOSM-12- 2018-0398
CIPD. (2019) People and machines: from hype to reality. London: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development.
Houghton, E. (2020) Strategic human resource management. Factsheet. London: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development. Available at: www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/hr/strategic-hrm-factsheet
Houghton, E. and Young, J. (2019) Organisational culture and cultural change. Factsheet. London: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development. Available at:
www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/culture/working-environment/organisation-culture-change
Para-González, L., Jiménez-Jiménez, D. and Martínez-Lorente, A.R. (2018), "Exploring the mediating effects between transformational leadership and organizational performance", Employee Relations, Vol. 40 No. 2, pp. 412-432. https://doi.org/10.1108/ER-10-2016- 0190
Parida, V., Sjödin, D. & Reim, W., 2019. Reviewing Literature on Digitalization, Business Model Innovation, and Sustainable Industry: Past Achievements and Future Promises. Sustainability, 11(2), p.391. Available at: http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/su11020391.
Sharp, S. and Green, M. (2020) Organisation development. Factsheet. London: Chartered Institute of Personnel and Development. Available at: www.cipd.co.uk/knowledge/strategy/organisational-development/factsheet
Wilmar Schaufeli. (2021) Engaging Leadership: How to Promote Work Engagement?, Frontiers in Psychology, 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.754556, 12